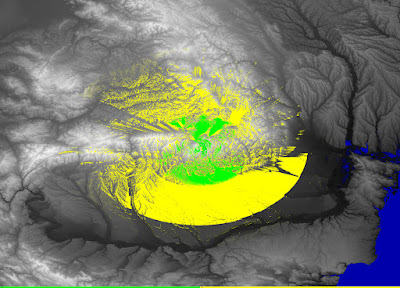
SPLAT! is a cross-platform, open-source software that can be used to analyze a radio link between two locations and to generate coverage maps of RF transmitters. Coverage maps are calculated using Longley-Rice Irregular Terrain Model (ITM) algorithm. SPLAT! can predict RF coverage for any frequencies between 20 MHz and 20 GHz. It is thus useful for ham radio, broadcast radio, terrestrial television and wireless networks.
To use SPLAT!, you need to know some parameters of the transmitter. These are the exact location (coordinates), antenna height, transmission frequency, polarization and effective radiated power (ERP). SPLAT! can then compute coverage maps. The procedure of installing SPLAT! is described in a previous article. You can generate two kind of maps. There is the regional coverage analysis mode that will output line-of-sight coverage map assuming all waves propagate in a straight line. There is also the path loss analysis mode that uses the ITM algorithm to compute either a field strength map or a received signal strength map.